Doppler Effect & Redshift
Interactive simulation of wavelength shifts from moving sourcesDirection: —
Shift: 0.00%
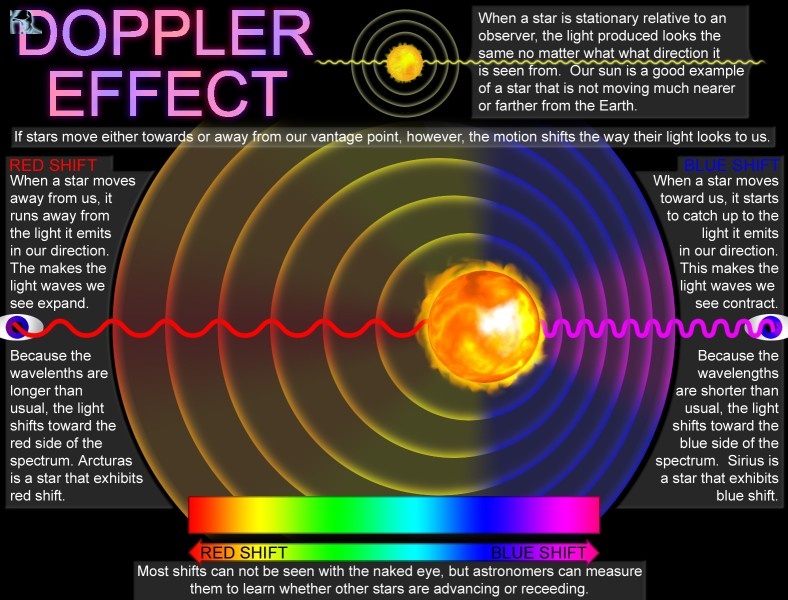
Wave Compression & Expansion
The Doppler Effect causes waves to compress when the source moves toward the observer (blueshift) and expand when moving away (redshift), changing both frequency and wavelength.
Blueshift
Approaching sources compress waves, increasing frequency and shifting light toward blue.
Redshift
Receding sources stretch waves, decreasing frequency and shifting light toward red.
Relativistic Effects
At high speeds, time dilation affects the observed frequency beyond classical predictions.
Astronomical Applications
Exoplanet Detection
Radial velocity method detects wobbles in star spectra
Galaxy Motion
Measuring recessional velocities and Hubble's law
Binary Systems
Studying orbital characteristics of star pairs
Cosmology
Understanding universal expansion and dark energy

