Black Hole Physics & Gravitational Lensing
Interactive simulation of spacetime curvature and light bending
Loading Black Hole Simulation...
Black Hole Properties
Rs = 2GM/c²
Schwarzschild Radius: 29.5 km
Event Horizon: 29.5 km
Photon Sphere: 44.3 km
Gravitational Time Dilation: 1.00x
Event Horizon: 29.5 km
Photon Sphere: 44.3 km
Gravitational Time Dilation: 1.00x
Current View
Observer Distance: 100 km
Viewing Angle: 45°
Redshift Factor: 1.00
Observer Distance: 100 km
Viewing Angle: 45°
Redshift Factor: 1.00
Gravitational Lensing
Einstein Radius: --
Magnification: --
Multiple Images: 0
Einstein Radius: --
Magnification: --
Multiple Images: 0
Accretion Disk
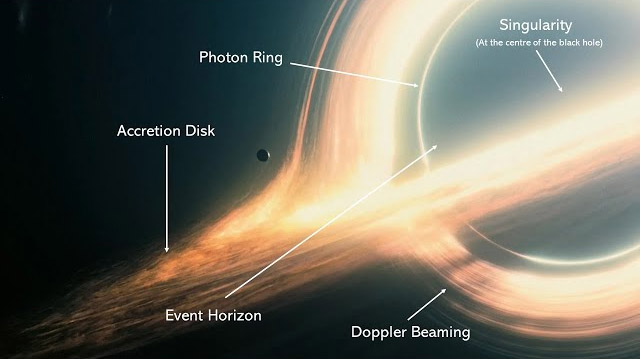
Spacetime Curvature
Black holes warp spacetime so severely that light paths are bent, creating multiple images of background objects and dramatic visual distortions.
Event Horizon
The point of no return where escape velocity exceeds light speed.
Photon Sphere
Orbit where light can circle the black hole multiple times before escaping.
Gravitational Redshift
Light loses energy climbing out of the gravitational well, shifting to red wavelengths.
Black Hole Types
Stellar
3-20 M☉
Formed from collapsing massive stars
Intermediate
100-10⁵ M☉
Mysterious formation mechanism
Supermassive
10⁵-10¹⁰ M☉
Found in galactic centers
Primordial
Microscopic to stellar
Formed in early universe
Another simulation of planetary orbits
Copernican's Cosmolgy
Interactive simulation of gravitational gradients and planetary disruption
Tidal Forces & Roche Limits

